Adam and Eve
Albrecht Dürer German
Not on view
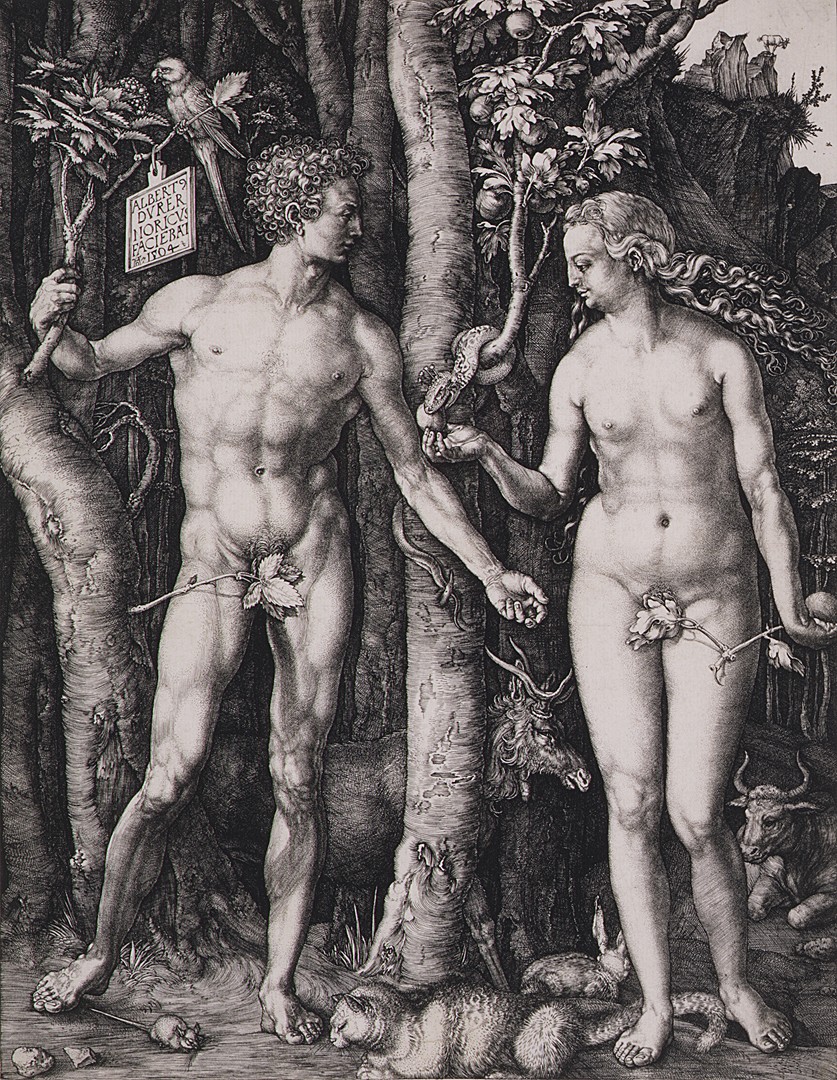
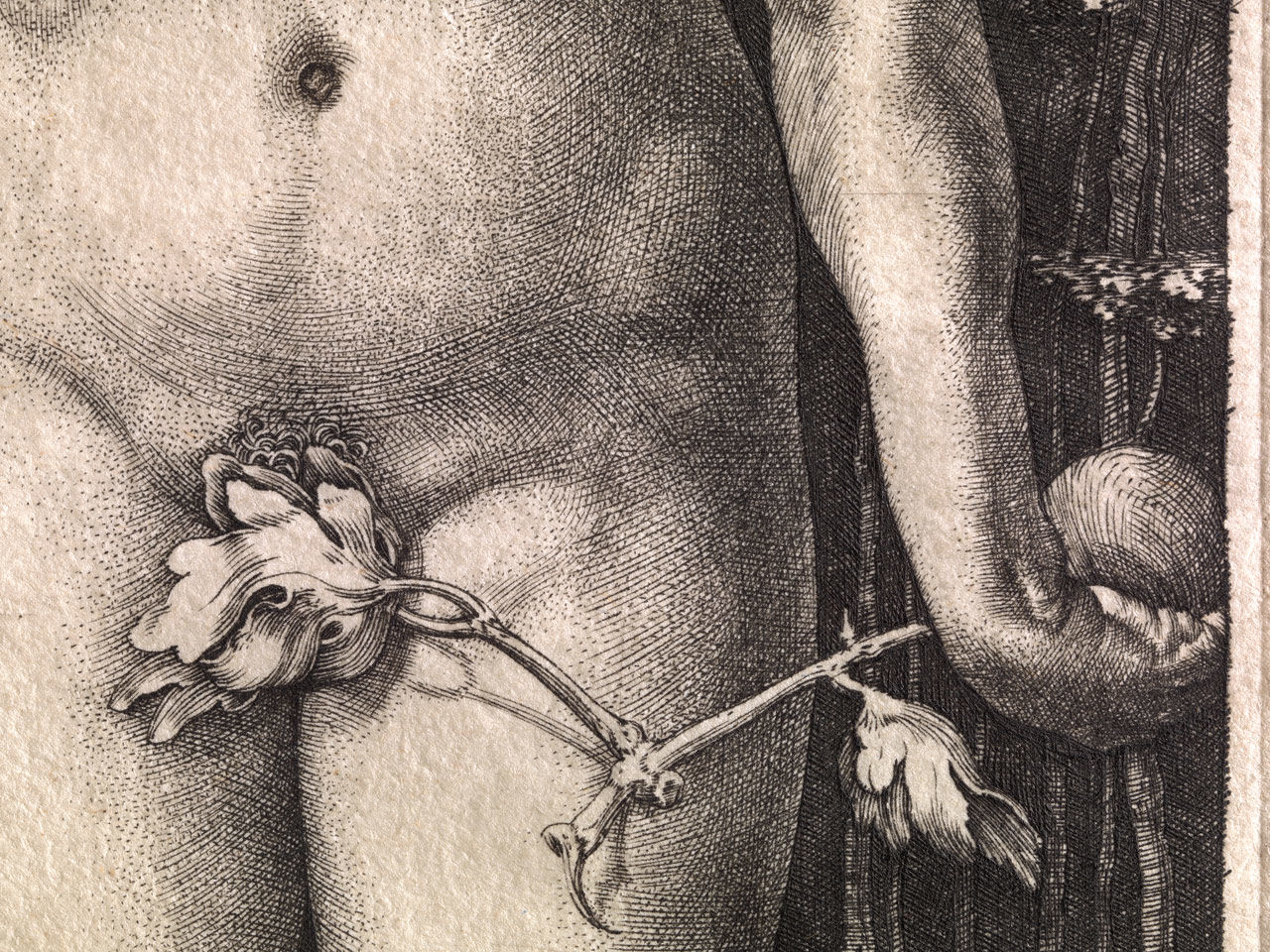
Throughout his life, Dürer was in thrall to the idea that the perfect human form corresponded to a system of proportion and measurements and could be generated by using such a system. Near the end of his life, he wrote several books codifying his theories, including the Underweysung der Messung (Manual of measurement), published in 1525, and Vier Bücher von menschlichen Proportion (Four books of human proportion), published in 1528 just after his death. Dürer's fascination with ideal form is manifest in Adam and Eve. The first man and woman are shown in nearly symmetrical idealized poses: each with the weight on one leg, the other leg bent, and each with one arm angled slightly upward from the elbow and somewhat away from the body. The figure of Adam is reminiscent of the Hellenistic Apollo Belvedere, excavated in Italy late in the fifteenth century. The first engravings of the sculpture were not made until well after 1504, but Dürer must have seen a drawing of it. Dürer was a complete master of engraving by 1504: human and snake skin, animal fur, and tree bark and leaves are rendered distinctively. The branch Adam holds is of the mountain ash, the Tree of Life, while the fig, of which Eve has broken off a branch, is from the forbidden Tree of Knowledge. Four of the animals represent the medieval idea of the four temperaments: the cat is choleric, the rabbit sanguine, the ox phlegmatic, and the elk melancholic.
Due to rights restrictions, this image cannot be enlarged, viewed at full screen, or downloaded.
This artwork is meant to be viewed from right to left. Scroll left to view more.